 Admin
Admin
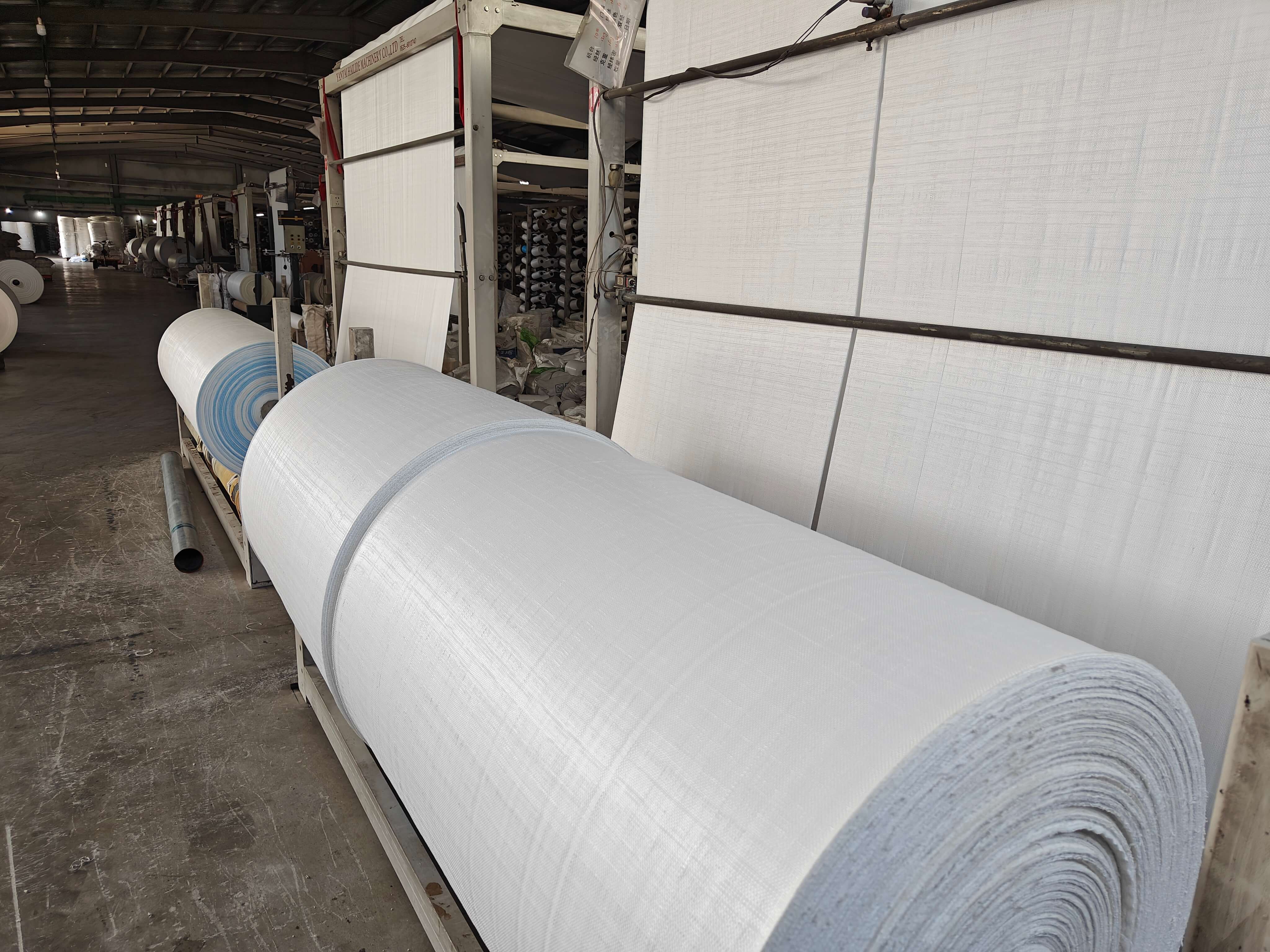
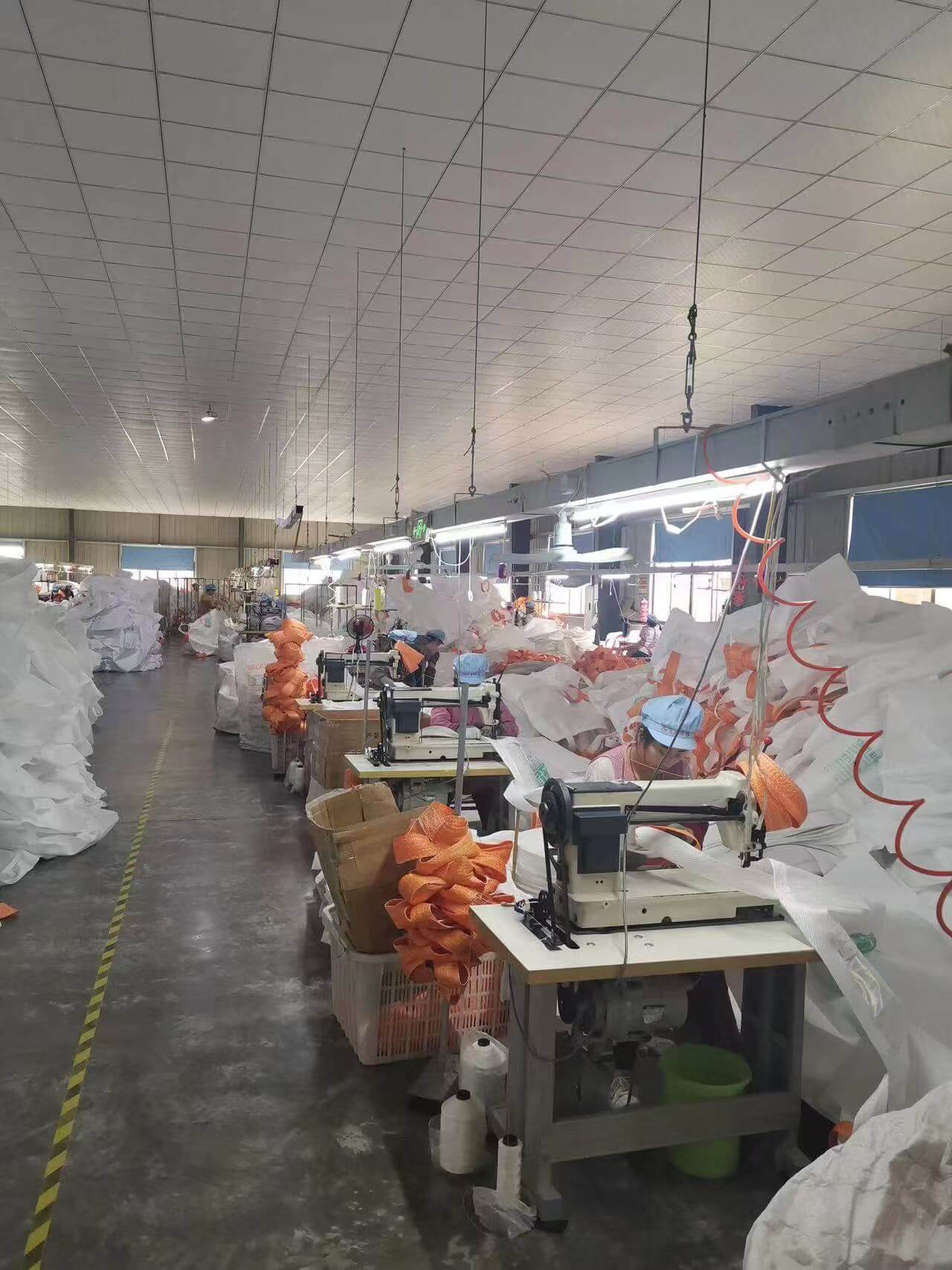
All industrial sectors involve handling materials and the right packaging can make a world of difference as it has a large impact on efficiency, safety, and cost-effectiveness. Ton bags—call them bulk bags, jumbo bags, or by their official title, FIBCs (Flexible Intermediate Bulk Containers)—are the backbone of bulk material transport and storage for powders, granules, and other free-flowing substances. But here's the thing: ton bags aren't a one-size-fits-all solution. Industry requirements have a lot of variance and need ton bags that match their specific type of operations for loading and unloading. Ton bags are used in nearly all types of industrial sectors for material handling, and all these industries require custom bags with special material and handles to ensure spillage-free loading and unloading of cargo or raw material. Therefore, it is worth sifting through the techs, design specifications and certification applicable to your industry before you choose your packaging. This is an overview into the main points you will have to consider to ensure your choices in ton bags are appropriate to your operations and regulations in force. Understanding the Purpose of Ton Bags Before discussing about the industry-specific requirements of ton bags we need to have a clear picture about why they are important for industries and what is their real function. A regular ton bad is manufactured from woven polypropylene and is able to carry bulk quantities of any cargo with a max limit of 1000kg. The design of the ton bags varies and the holding handles and lining materials of ton bags vary since they are customized according to industrial application. Ton bags are used in almost every industrial sector, but the industries that depend heavily on their usage are construction and the agricultural storage industry. What To Consider While Selecting a Ton Bag Assessing the Material Nature for Loading in Ton Bag The most crucial factor that you should keep in mind when you decide to buy a ton bag is the material that you plan on transporting or shifting to another location. If the material is in a fine powder form like cement, flour, etc., then the powder can easily leak, and the ton bag should have an inner lining with sift-proof seams to prevent the leaking of material. However, these inner linings are not required if you intend to transport grains, seeds, or pellets. Materials that need a moisture-free environment to retain quality should be loaded in ton bags that have a laminated coating or polyethylene liners that prevent the humidity from seeping in. Materials that have sharp edges like gravel stone need ton bags made of tougher and thicker fabric with a high GSM (grams per square meter). You also need to know about the material's density. A light material but which occupies space such as polystyrene beads will require a large capacity ton bag to store them but it does not have to have a high load resistance. But for dense objects like metal powder a bag with a solid structural integrity is needed. Choosing Adequate Ton Bag Design and Construction Ton bags have a wide range of designs that are suited for specific storage and transporting scenarios. U-panel bag is ton bag that is a perfect choice for genral storage use as it delivers an even balance of strength and shape retention. Another type of ton bag is a circular bag, which is manufactured from a seamless, tubular body. This shape reduces the risk of the side seams splitting open. In cases where space is congested in storage or during transport, the baffle bag is the right choice since it has a compact square shape that allows it to be tucked easily. Four-panel ton bags, which have their internal space divided into four regions, are usually used for packing material tightly together. The design of the ton bag should also make filling and unloading of material convenient because in industrial sites loading efficiency is linked with greater operational productivity. Ton bags with spout tops allow for a cpntrolled filling procedure minimizing spills. But if you prefer fast loading or manual loading, then open-top designs should be your choice.Other design aspects comprise of the use of bottom spouts, flat bottom, and discharge chutes that helps in the effective unloading process as well as minimizes chances of spillage. Industry-Specific Standards Sanitation is vital to the food and pharmaceutical industries. Bags for the food or pharmaceutical industry must be manufactured within a clean room environment, and will generally be specified to be certified to either ISO 22000 or FDA compliance. They usually have food grade liners, and the final inspection and construction will use a process that eliminates any possible risks for contamination. The chemical industry deals with hazardous or reactive materials. In this case, ton bags must be UN certified for the movements of dangerous goods, and would go through testing protocols for chemical resistance, bursting strength, and also impact protection to contain and protect unstable materials during handling. For construction and mining, the two most important factors are strength and durability. Sturdiness and ruggedness are paramount in construction and mining activities. Ton bags here must withstand adverse conditions, UV exposure, and rough mechanical handling. Reinforced loops, high GSM fabric, and extra stitching are among the common requirements in this environment. Agriculture mainly relies on ton bags to store and transport seeds, fertilizers, and animal feed. They must be moisture-resistant yet breathable to allow for the moisture present in plant products to evaporate. Cost-effectiveness Saving trnaspotation and handling costs is always at the forefront of a company's agenda and the lifecycle cost of each bag contributes a lot to this. A long usage life means that the bag can be reused a lot and this means less cost of replacement. A single-use bag looks economical, but in an industry where bags are able to be reused multiple times, investing in a higher-grade FIBC can lead to savings in the long run. Customization may drive up the initial cost, but can assist with handling, promote speed in operations, and ensure branding. Printed labels, barcoding, or color stitching will assist in logistics and inventory control, especially for larger operations. Partnering with the Right Supplier Last but not the least you need to select a supplier that gives you quality packaging for every kind of product lineup. Reputable manufacturers will give you a guarantee about the superior quality of their products as well as technical support. The guarantee can be with multiple quality certifications. Moreover, a reliable supplier will go the extra mile to customize the dimensions of the bag to match your industry needs. A quality vendor will also deliver the order consistently without any delay keeping your packaging and transporting operations seamless. Handling Design The way in which a ton bag will be handled—lifted, transported, filled, and emptied—should directly affect your choice of ton bag. Bags come with different loop configurations, be it cross-corner loops, side-seam loops, or lifting sleeves, to fully relate to the different types of lifting equipment. Forklift compatibility, sling handling, or crane usage should all be considered. Safety design should also be taken into consideration by an operator. Properly labeled bags with safety marks, in correct load ratings, and easy handling instructions reduce the chances of accidents on-site. Areas with combustible gases or dust may need to use antistatic bags or conductive ton bags to prevent electrostatic discharge. These parameters of how the ton bag shall be handled: lifted, transported, filled, and emptied should directly determine your selection. Bags have different forms of loops for their configuration, such as cross-corner loops, side-seam loops, or lifting sleeves. These forms ensure compatibility with handling equipment like forklifts, sling handling, or cranes. It also entails a design that considers the safety of the operator. Safe labels, correctly rated bags according to load, and clear instructions on handling everyone reduce the accident chances on-site. Antistatic or conductive ton bags may be incorporated where dust or flammable gas exists to avoid the incidents of electrostatic discharges. Conclusion Picking out the right ton bag for your business is not as easy as you think, it is not just grabbing any old sack off the shelf—there’s a lot more to it! You gotta think about what you’re actually putting in it (grains, chemicals, rocks, you name it), how you’ll use it, and all those rules and weather issues that might pop up. The right bag honestly makes everything smoother—fewer headaches, safer for your team, and could even save you some cash down the line. FAQs Q: What aspects to take into account when choosing a ton bag for my industry? A: Key factors include the type and weight of material being handled, environmental conditions, industry-specific regulations, and whether the bag will be reused or is for single use. Q: Are there different types of ton bags for different applications? A: Yes, ton bags have different styles which include U-panel, baffle, and circular types. They are all tailored into various requirements such as enhanced form retention, space efficient or tiny containing material. Q: Do I need a special ton bag for food, chemicals, or hazardous materials? A: Absolutely. Industries like food and chemicals require certified ton bags—such as FDA-approved or UN-certified types—to ensure safety, hygiene, and regulatory compliance.
 Jul 04 2025
Read More
Jul 04 2025
Read More